Multiple choice: Check your answers by clicking on them.
Fill in the gaps. Toggle down to check your results.
1. The average molecular weight of lysine is 146.19 g/mol (C6H14N2O2). Calculate the monoisotopic masses of the here depicted isotopes of lysine. Note the exchanges of 12C isotope against 13C isotope, which are marked in the image below. Match the numbers in the boxes with the possible solutions below.
Masses of the most abundant isotopes of C, H, N and O:
12C = 12.00000
13C = 13.00336
1H = 1.00782
14N = 14.00307
16O = 15.99491
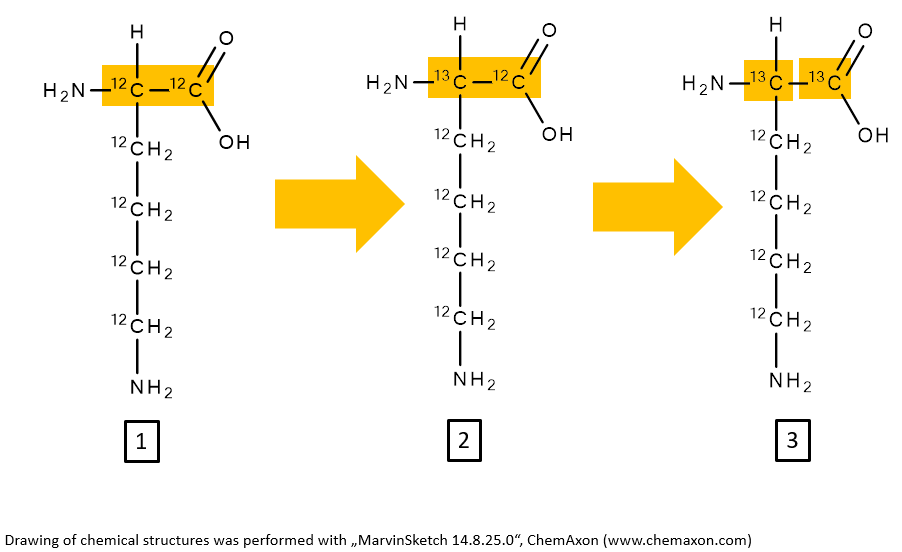
a) 148.100552 Da, b) 146.10552 Da, c) 145.09770 Da, d) 147.10552 Da
Solution
1b, 2d, 3a
2. The process of mass spectrometric analysis consists of different steps. Match the provided options with the possible solutions below.
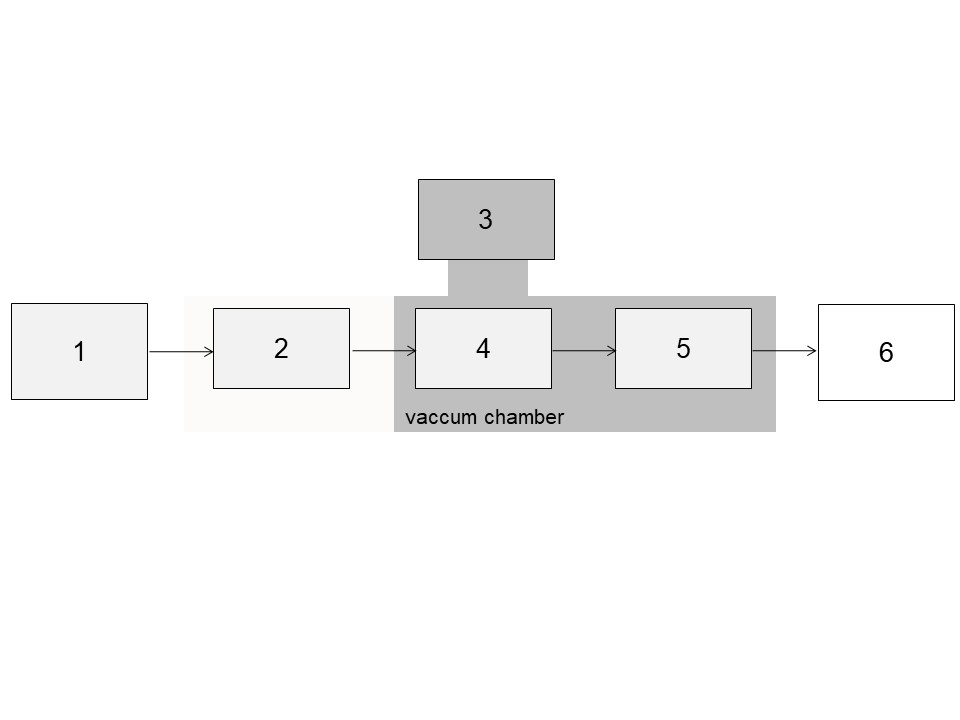
a) detector, b) vacuum pump, c) recording, d) mass analyzer, e) ion source, f) sample inlet
Solution
1f, 2e, 3b, 4d, 5a, 6c
3. What does TIC?
Solution
Total Ion Chromatogram
4. Write out EIC.
Solution
Ectracted Ion Chromatogram
5. Match the numbers in hte boxes with a „molecular ion“-label as well as the „charge state“ of the lysines. The green circle depicts a positive and the red one a negative charge.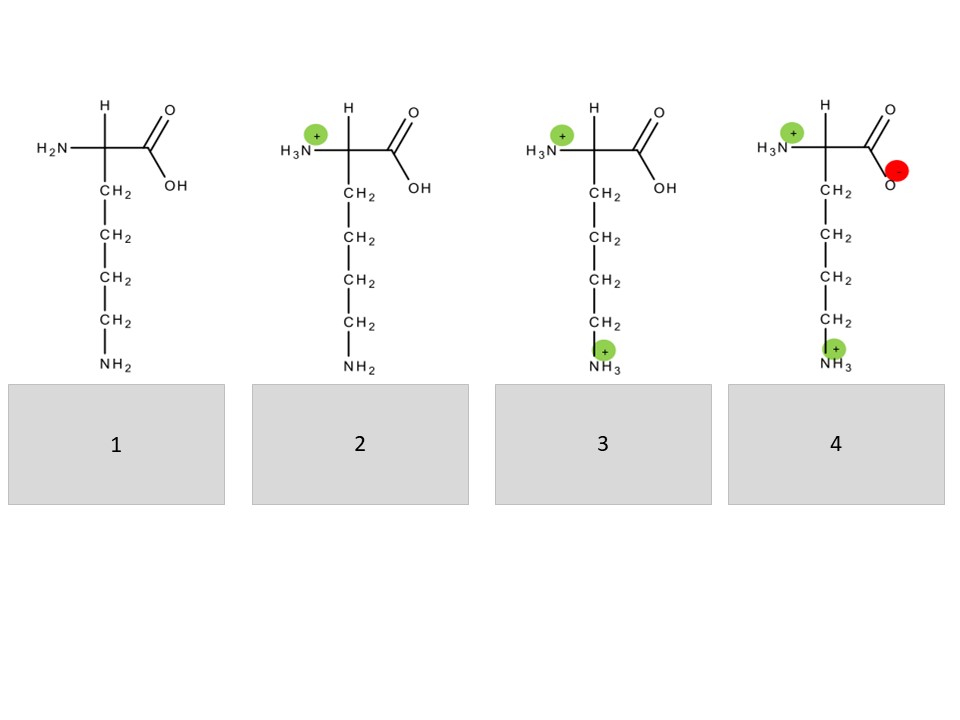
a) singly charged (2x), b) doubly charged c) M, d) [M+2H]2+, e) [M+2H-1H]+, f) [M+H]+, g) uncharged
Solution
1gc, 2af, 3bd, 4ae
6. Each ionization technique is suitable for specific applications with regard to the analyte’s molecular weight and polarity. Match the provided ionization techniques with the respective field.
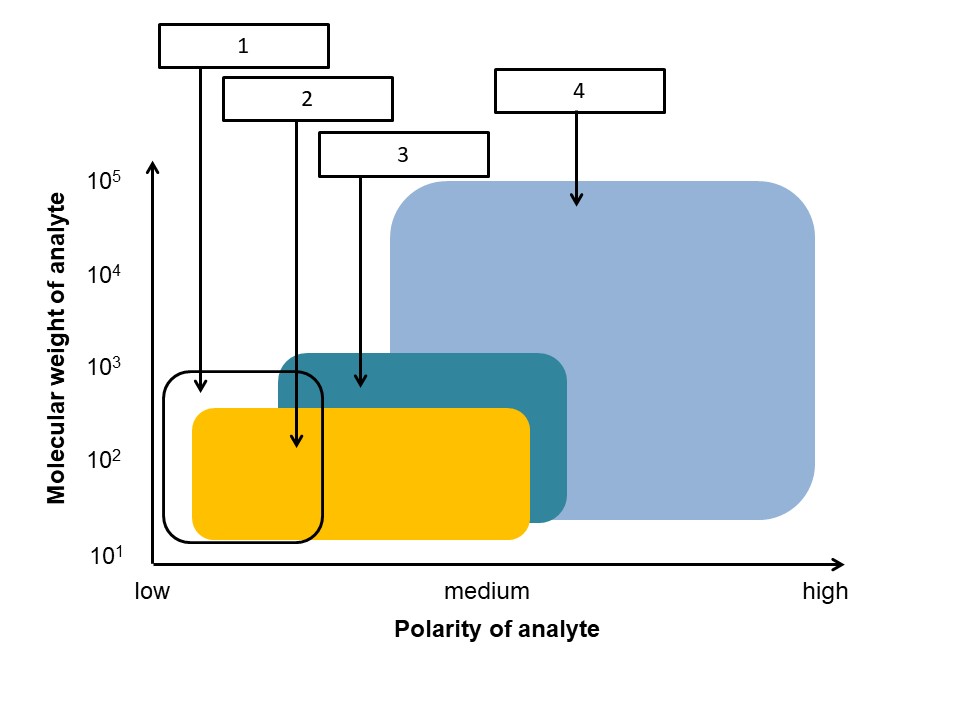
a) APCI, b) ESI, c) EI/ CI, d) APPI
Solution
1c, 2d, 3a, 4b
7. Label the depicted graphs, which are obtained using an LC-MS experimental setup. (Software used for data evaluation: MassHunter Qualitative Analysis B. 03.01, Agilent Technologies)

a) TIC, b) RIC, c) EIC, d) mass spectrum, d) ionogram
Solution
1a, 2c, 3d
8. An analyte with the sum formula C5H10N2O3 has an monoisotopic mass of 146.06913. Calculate:
a) [M+H]+
b) [M+2H]2+
c) [M-H]–
d) [M+Na]+
e) [M-2H+Na]–
Use:
H = 1.00782, Na = 22.98980
Solution
a) 147.07695, b) 74.042385, c) 145.06131, d) 169.05893, e) 167.04329
9. An analyte has the sum formula C6H9N3O2. The average molecular weight is 155.15 g/mol. Calculate the monoisotopic mass using the following masses of isotopes:
12C = 12.00000
1H = 1.00782
14N = 14.00307
16O = 15.99491
Solution
155.06941
10. An analyte has the sum formula C14H12O3. The calculated monoisotopic weight is 228.07863. It is mass spectrometrically detected to carry a single positive charge in the form of a proton, i.e. [M+H]+. The calculated accurate m/z would therefore be 229.08645. The actual mass spectrometrically detected m/z is however 229.08603.
Calculate the mass deviation between calculated and detected m/z in ppm (parts per million) using the following equation:
Mass deviation = [(calculated−detected) calculated]×1000000
Give the calculated mass deviation with two decimal places (i.e. 0.00).
Solution
1.83
11. The m/z´s of analytes in your sample only differ by 0.1 m/z, i.e 1140 and 1140.1. What mass spectrometric resolution is required at the very least to resolve the signals.
Use the following equation for the calculation: Resolution R = m/(m2-m1)
Solution
11400
12. a) Which ionization technique uses a beam of high energy electrons to generate radical cations, i.e. M•+ (M= the analyte)?
M + e- → M•+ + 2 e-
b) Which one generates radical anions, i.e. M•-?
M + e- → M•-
Solution
a) electron ionization, b) electron capture ionization
